BECE 2005 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Hydrogen is represented by the chemical symbol H₂. This symbol represents
Solution: H₂ denotes a single molecule composed of two hydrogen atoms bonded together, not separate molecules, elements, or ions.
2. A metal expands when there is
Solution: Heating increases atomic vibration, causing atoms to occupy more space and expand the metal. Electron count, potential energy, or atom proximity don't directly cause expansion.
3. A safety device which opens an electrical circuit to prevent too much current from passing through the circuit is the
Solution: A fuse contains a wire that melts when excess current flows, breaking the circuit. Earth wires ground excess charge, lightning conductors divert strikes, and switches manually control circuits.
4. An object is placed 20 cm in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the object and the image is
Solution: In a plane mirror, the image forms as far behind the mirror as the object is in front. Thus, total distance = 20 cm (object to mirror) + 20 cm (mirror to image) = 40 cm.
5. In which of the following circuit diagrams below will the bulb light?
Solution: A bulb lights only in a complete (closed) circuit with a power source and uninterrupted path for current. Option B depicts such a circuit.
6. The source of all forms of energy can be traced to
Solution: Sunlight drives photosynthesis (chemical energy), weather (wind/water energy), and fossil fuel formation. Other options are secondary energy manifestations.
7. When a mango is falling from a tree, its potential energy is changed to
Solution: As the mango falls, height (and potential energy) decreases while speed (kinetic energy) increases. Minor sound/heat may occur, but kinetic energy is primary.
8. Electricity is used by appliances to do work. This means that electricity is a form of
Solution: Electricity transfers energy to appliances to perform work (e.g., heating, motion). Force is a push/pull, while generators and machines utilize energy.
9. A force of 2N moves a body through a distance of 10 m. Calculate the work done.
Solution: Work = Force × Distance = 2 N × 10 m = 20 J (joules). Energy transfer occurs in the direction of force application.
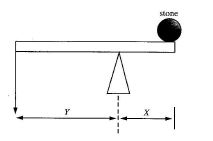
The diagram below shows a lever system used to move a stone. Use it to answer Questions 10 and 11
10. The diagram below shows a lever system used to move a stone. The distance X is the
Solution: In levers, "load distance" (X) is the distance from the fulcrum to the load (stone). Effort distance is from fulcrum to where force is applied.
11. Less effort is required to move the stone when the
Solution: Mechanical advantage increases when effort distance (Y) > load distance (X), reducing required effort. Lever principle: Effort × Y = Load × X.
12. An omnivore is an animal that feeds on
Solution: Omnivores consume both plant and animal matter ("all kinds of food"). Food preparation (raw/fresh/cooked) doesn't define dietary classification.
13. A meal containing all the essential nutrients in the right amounts is said to be
Solution: A "balanced" diet provides carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals in proper proportions for health. Other options describe taste, preparation, or single components.
14. The disease associated with insufficient intake of proteins in children is
Solution: Kwashiorkor results from severe protein deficiency, causing edema and stunted growth. Goiter (iodine), rickets (vitamin D), and scurvy (vitamin C) involve other nutrients.
15. When testing for proteins in a food substance using Fehling’s solution, the expected colour change is
Solution: Fehling’s test detects reducing sugars (not proteins). For proteins, Biuret test is used (violet/purple). Note: Original document lists "D. brick-red" in solutions, implying a possible question error. Standard protein tests use Biuret (purple), not Fehling’s.
16. The substance that enables green plants to trap sunlight for the manufacture of food is
Solution: Chlorophyll (a pigment in chloroplasts) absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are organelles containing chlorophyll; phloem/xylem transport nutrients/water.
17. In man, the conversion of poisonous substances into harmless forms takes place in the
Solution: The liver detoxifies chemicals (e.g., ammonia → urea), metabolizes drugs, and produces bile. Kidneys filter waste; bladder stores urine; duodenum digests food.
18. Which of the following life processes is represented by the equation below?
Solution: Cellular respiration breaks down glucose with oxygen to release energy (ATP), producing CO₂ and H₂O. Photosynthesis reverses this process.
19. Chlorine gas is passed through water during purification to
Solution: Chlorine disinfects water by destroying bacteria/viruses. Settling particles involves coagulation (e.g., alum); softening removes minerals; taste is improved by aeration/filtration.
20. Arrange the following sources of water in the order of increasing contamination
I. Rain
II. Stream
III. Well
IV. Borehole
Solution: Rainwater (I) is least contaminated (atmospheric). Borehole (IV) is deep groundwater, then shallow well (III), and streams (II) are most exposed to pollutants.
21. A solution in which no more solute will dissolve at a given temperature is said to be
Solution: A saturated solution holds the maximum solute at that temperature. Concentrated/dilute describe amount dissolved; homogeneous means uniform mixture.
22. A clear solution of sugar was cooled from 100°C to 25°C. Some solid sugar was seen to have formed out of the solution after cooling. This shows that sugar
Solution: Solubility increases with temperature. Cooling reduces solubility, causing excess sugar to crystallize. Sugar dissolves in both hot/cold water, but better in hot.
23. Water is sometimes referred to as a universal solvent because it
Solution: Water dissolves ionic/polar compounds due to its polarity. It isn't the purest (contains dissolved gases/minerals) nor exclusive to living cells, but its solvent versatility is unmatched.
24. The charge of sulphur in the compound \( SO_2 \) is
Solution: Oxygen has -2 charge each. For SO₂: S + 2(-2) = 0 (neutral molecule). Thus, S = +4.
25. The part of the soil that supports plant growth is that part which
Solution: Humus (decayed organic matter) improves soil structure, nutrient retention, and water-holding capacity, directly supporting plant growth.
26. Plants do not grow well in gravel because the
Solution: Gravel has large pores that drain water quickly and lacks organic matter/nutrients. Roots need sustained moisture and nutrients, which gravel cannot provide.
27. Which of the following parasites lives in the blood of humans?
Solution: Plasmodium (malaria parasite) infects red blood cells. Lice/tick are ectoparasites; tapeworms live in intestines.
28. The carrier of the malaria parasite is the
Solution: Female Anopheles mosquitoes transmit Plasmodium while feeding on blood. Males feed on nectar; black flies spread river blindness; tsetse flies spread sleeping sickness.
29. Which of the following practices is a method of controlling guinea worm disease?
Solution: Guinea worm larvae enter through skin when wading in water. Wearing footwear blocks transmission. Bush clearing targets vector habitats for other diseases (e.g., malaria).
30. The humidity of the atmosphere is measured with
Solution: Hygrometers measure humidity. Anemometers measure wind speed; barometers measure air pressure; hydrometers measure liquid density.
31. How long does it take the moon to move completely around the earth?
Solution: The sidereal month (complete orbit relative to stars) is ~27.3 days, often rounded to 28 days in basic science. The synodic month (full moon cycle) is ~29.5 days.
32. Steel is an example of a
Solution: Steel is an alloy (solid solution) of iron (solid) and carbon (solid), making it a solid-solid mixture.
33. Which of the following elements is a metal?
Solution: Sodium (Na) is a soft, reactive metal. Carbon/Nitrogen/Sulphur are non-metals.
34. Metals that are usually used to make ornaments have low
Solution: Ornament metals (e.g., gold, silver) resist tarnishing/corrosion due to low reactivity. They are highly conductive, ductile, and malleable.
35. The food processing method in which germs are prevented from multiplying by applying a low temperature is
Solution: Refrigeration slows microbial growth by reducing temperature. Canning uses heat sterilization; drying/pickling remove water or alter pH.
36. The function of blood platelets is to
Solution: Platelets (thrombocytes) form clots to stop bleeding. CO₂ transport is by plasma/RBCs; disease fighting by WBCs; temperature regulation involves blood flow/sweating.
37. A fish is able to swim with little resistance in water because it has
Solution: Streamlined shape minimizes drag by allowing water to flow smoothly. Fins aid propulsion; gills are for respiration; oxygen use is unrelated to resistance.
38. When a person jumps up, he/she is able to come down because of the
Solution: Gravity accelerates the person downward after the jump. Magnetic force affects compasses, not free fall; atmospheric effects are negligible for short jumps.
39. A metal displaces 5.0 cm³ of water when completely immersed in water. If the mass of the metal is 35.0 g, calculate its density.
Solution: Density = Mass / Volume = 35.0 g / 5.0 cm³ = 7.0 g cm⁻³. Displaced water volume equals the metal’s volume.
40. Oxygen from the air is able to get into the blood by
Solution: Oxygen moves from high concentration (alveoli) to low concentration (blood) via diffusion. Osmosis involves water; capillarity is liquid rise in tubes; suction is mechanical.
1. Question 1
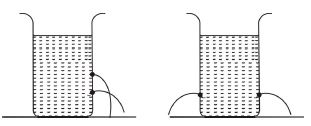
1. (a) In an experiment, a pupil took two empty Milo tins and made holes in their sides as shown in the diagram above. The pupil then filled the Milo tins with water.
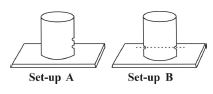
(i) Draw and label the diagrams to show what the pupil will observe in set-up A and set-up B
(ii) Explain the observations in set-up A and set-up B
(iii) What is the aim of set-up A?
(iv) What is the aim of set-up B?
(b) In an experiment, equal volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid (solution A) and dilute sodium hydroxide (solution B) are mixed together to form solution C.
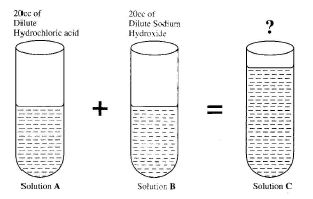
(i) What is the volume of solution C?
(ii) Red litmus paper and blue litmus paper are dipped in turns into solutions A, B and C. State the observations you will make in all six cases
(iii) Give the name of the reaction that took place between solution A and solution B
(iv) Identify solution C
(v) State what will happen when solution C is heated.
(c) The table below gives the steps that were followed in an experiment to test for starch in a green leaf freshly taken from a tree.

(i) State the reason for carrying out each of the activities in stages I, II and III.
(ii) What happens when the leaf is dipped in iodine solution?
(iii) Give the colour changes of the leaf from the beginning of the experiment to the end of the experiment.
(iv) Why is the alcohol warmed indirectly in a water bath?
(v) Explain what will be observed if the test is carried out on a leaf taken from a plant kept in a dark room for 1 day.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1. (a) (i)
(ii) Set-up A: Water jets out farther from the lower hole than the upper hole because liquid pressure increases with depth.
Set-up B: Water jets out equally from both holes because liquid pressure is equal at the same depth.
(iii) To demonstrate that liquid pressure increases with depth.
(iv) To demonstrate that liquid pressure at the same depth is equal.
(b) (i) 40 cc
(ii) - Red litmus in A: remains red
- Blue litmus in A: turns red
- Red litmus in B: turns blue
- Blue litmus in B: remains blue
- Red litmus in C: turns purple
- Blue litmus in C: turns purple
(iii) Neutralization reaction
(iv) Sodium chloride solution (common salt solution)
(v) Water evaporates, leaving solid crystals of sodium chloride.
(c) (i) - Stage I: Kills cells and stops photosynthesis.
- Stage II: Removes chlorophyll.
- Stage III: Washes off alcohol and softens leaf.
(ii) Turns blue-black where starch is present.
(iii) Green → pale yellow/light brown/cream → blue-black.
(iv) Alcohol is flammable; indirect heating prevents explosion.
(v) No blue-black color (starch absent due to lack of photosynthesis in darkness).
2. Question 2
2. (a) (i) Define respiration.
(ii) Give two differences between photosynthesis and respiration.
(b) (i) List the chemicals used in the preparation of carbon dioxide in the laboratory.
(ii) How would you test for carbon dioxide in the laboratory?
(c) (i) State four effects of a force on a body.
(ii) A horizontal force of 250 N is applied to pull a piece of wood lying on a smooth surface through a distance of 20 m. Calculate the work done.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2. (a) (i) Process where oxygen is delivered to cells, producing carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
(ii) 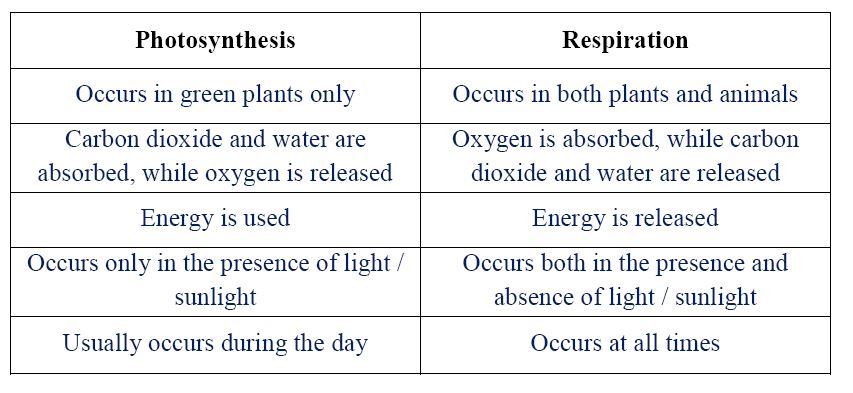
(b) (i) Dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO₃).
(ii) Bubble through limewater; turns milky if CO₂ present.
(c) (i) - Starts/stops motion
- Changes speed
- Changes direction
- Changes shape
(ii) Work done = Force × Distance = 250 N × 20 m = 5000 J.
3. Question 3
3. (a) (i) Give two differences between a vein and an artery.
(ii) State two functions of red blood cells.
(iii) Mention two diseases associated with the circulatory system.
(b) (i) Classify: Cooking food, melting candle, melting ice, rusting iron, dissolving sugar, burning wood.
(ii) Explain the basis of the classification.
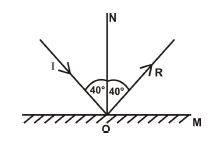
(c) (i) State the laws of reflection.
(ii) Draw a ray diagram for 40° incidence on a plane mirror.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3. (a) (i)
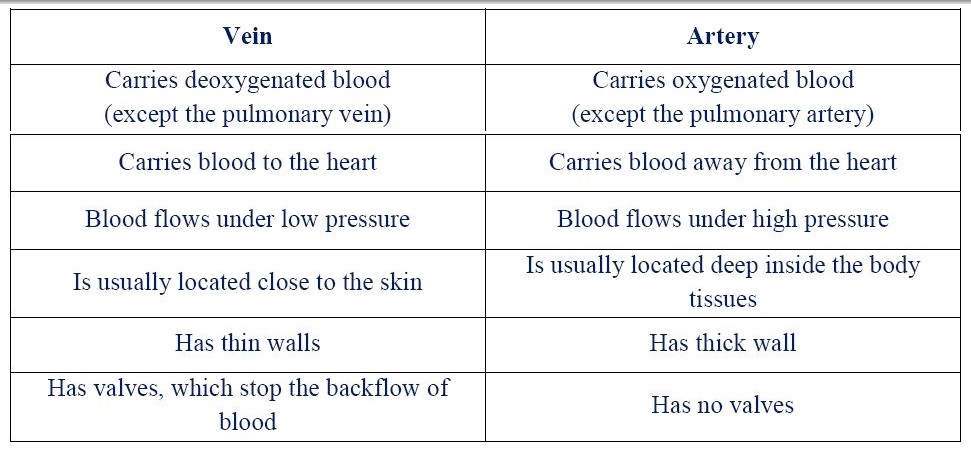
(ii) - Transports oxygen
- Regulates body temperature
(iii) - Hypertension
- Anemia
- Leukemia
- Malaria
(b) (i) Physical: Melting candle, melting ice, dissolving sugar.
Chemical: Cooking food, rusting iron, burning wood.
(ii) Physical: Reversible, no new substance.
Chemical: Irreversible, new substance formed.
(c) (i) 1. Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection.
2. Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in same plane.
(ii)
4. Question 4
4. (a) (i) Explain vegetative reproduction.
(ii) State two differences between sexual and vegetative reproduction.
(iii) Give one advantage of vegetative reproduction.
(b) (i) Name solvents for: Oil paint, fat, common salt, plant pigments.
(ii) What is a substance dissolved by a solvent called?
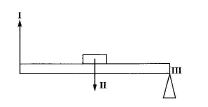
(c)
(i) What class of simple machine?
(ii) Name parts I, II, III.
(iii) Give two real-life examples of this machine.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) Asexual reproduction using plant parts (e.g., stems, roots).
(ii)
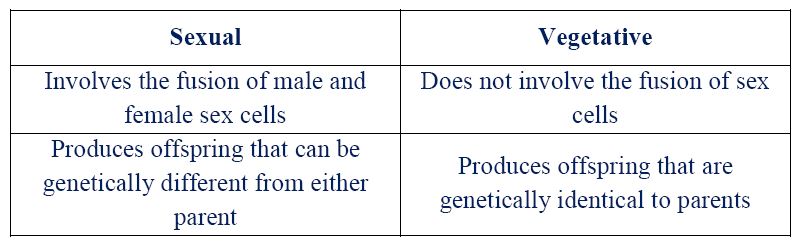
(iii) Faster growth/preserves parent traits.
(b) (i) - Oil paint: Turpentine/kerosene
- Fat: Ether
- Common salt: Water
- Plant pigments: Alcohol
(ii) Solute
(c) (i) Second-class lever
(ii)
I: Effort
II: Load
III: Fulcrum
(iii) Wheelbarrow, nutcracker, bottle opener.
5. Question 5
5. (a) (i) Give two differences between a parasite and a vector.
(ii) Name three endoparasites and their hosts.
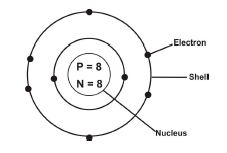
(b) Atom: 8 protons, 9 neutrons.
(i) Draw atomic structure.
(ii) Charge if it gains 2 electrons? (Show working).
(c) (i) Draw layered liquids: X=1.5 g/cm³, Y=3.0 g/cm³, Z=1.0 g/cm³.
(ii) Calculate volume of 300g petrol (density=0.9 g/cm³).
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
5. (a) (i)
parasite:Causes disease directly, Lives in/on host
VectorTransmits disease pathogen, Lives independently
(ii) - Tapeworm → Humans
- Plasmodium → Humans
- Roundworm → Humans
Liver fluke → humans
Guinea worm → humans
(b) (i)
(ii) Charge = (8+) + (10−) = −2.
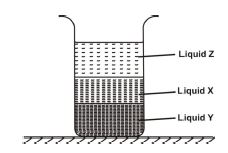
(c) (i) Layers (bottom to top): Y (densest), X, Z (least dense).
(ii) Volume = Mass/Density = 300g / 0.9 g/cm³ = 333.33 cm³.